PROJECT DETAILS
- Date May 8, 2024
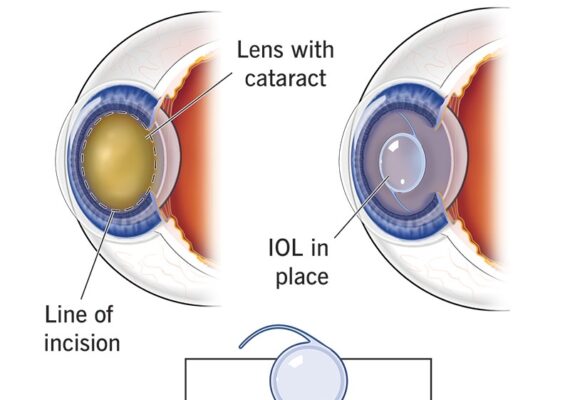
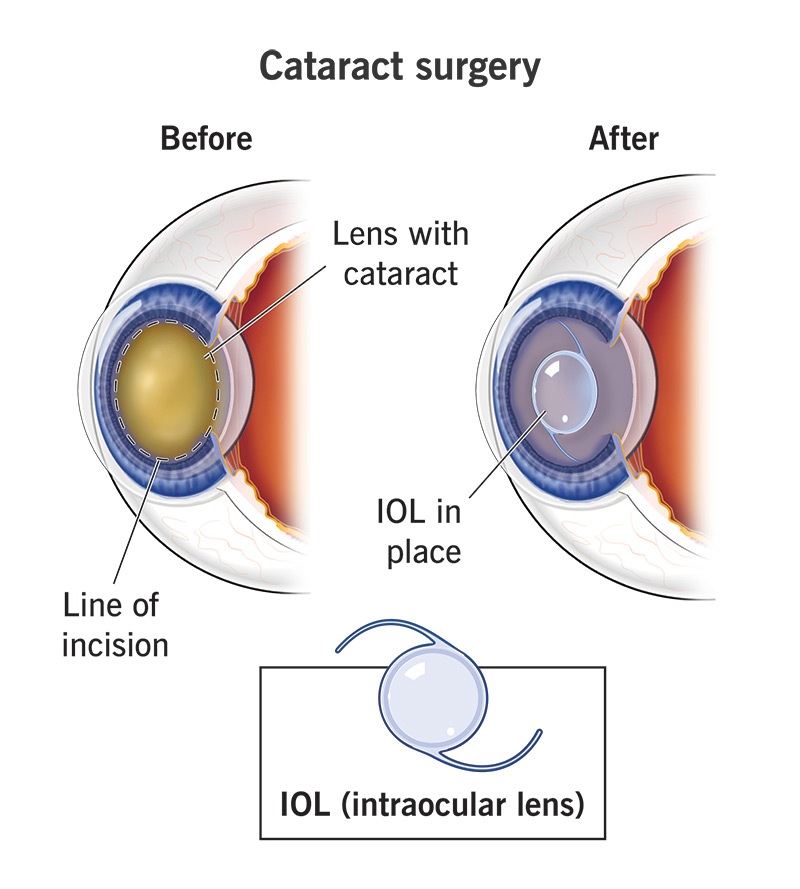
Cataract surgery is a common and highly effective procedure aimed at restoring vision impaired by cataracts, which are the clouding of the eye’s natural lens. During the surgery, the cloudy lens is removed and replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
The process typically begins with a comprehensive eye examination to assess the cataract’s severity and determine the most suitable IOL for the patient’s needs. Before surgery, the patient may undergo measurements of the eye’s dimensions to ensure proper IOL selection.
Cataract surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia and is often completed on an outpatient basis. The surgeon makes a small incision in the eye and uses ultrasound energy to break up the cloudy lens, which is then removed through suction. Once the cataract is removed, the IOL is inserted into the eye to replace the natural lens.
After surgery, patients are usually prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and manage inflammation. Recovery is typically quick, with many patients experiencing improved vision within a few days. It’s essential for patients to attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing and vision progress.
Cataract surgery is considered safe and highly successful, with the vast majority of patients achieving improved vision and quality of life following the procedure.